アルツハイマー病治療薬の開発に期待!! 2023/12/26
Aβオリゴマーの毒性から神経細胞を保護するペプチド / p3-Alcβ37, p3-Alcβ9-19
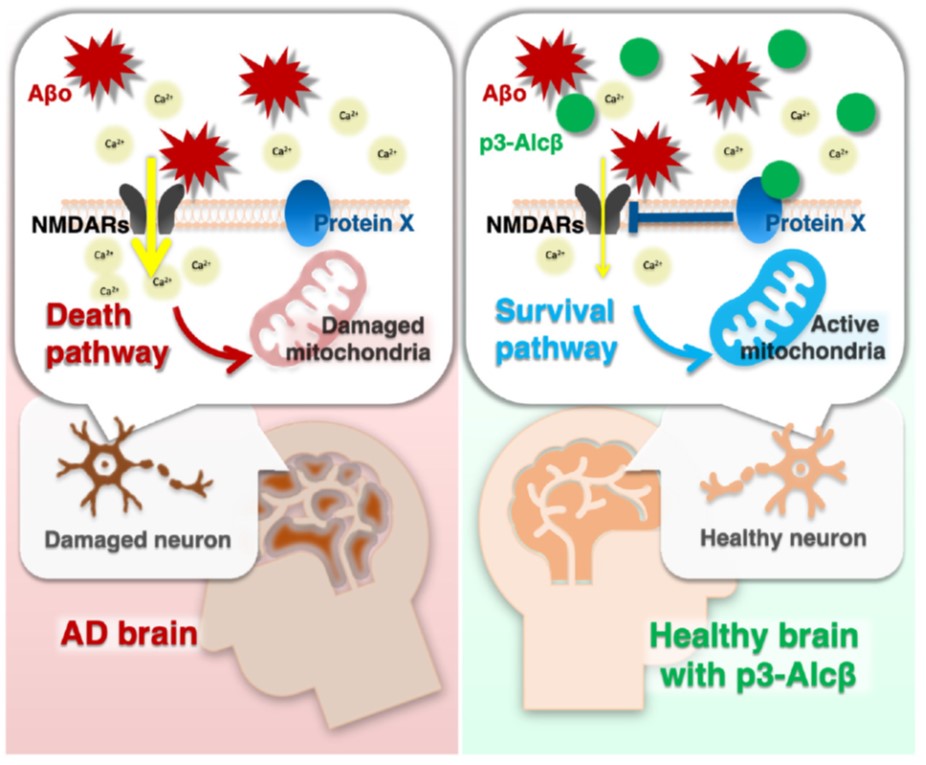
p3-Alcβペプチドは,北海道大学の鈴木利治特任教授らによって開発された,Aβオリゴマーの毒性に対して,神経細胞のミトコンドリア活性を高めることで,神経細胞を保護する作用を持つペプチドです1)。
Aβオリゴマーは,神経細胞のNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体に作用して,細胞内に過剰なCa2+を流入させ,その結果,ミトコンドリアの生存率を低下させて,神経細胞死を導くことが知られています。本ペプチドを神経細胞に作用させると,Ca2+の流入を抑えることで,ミトコンドリアの生存率低下を抑制し,神経細胞が保護されることが明らかとなりました。また,本ペプチドをマウスやサルに末梢投与すると,ペプチドは脳内に移行して,脳内のミトコンドリア機能が回復することが確認されています。今後,神経細胞の機能を保護するという新しいメカニズムのアルツハイマー病治療薬として開発が進むことが期待されています。
| Code | 品名 | 容量 |
| 4485-v | p3-Alcβ37 | 0.5 mg |
| 4510-v | p3-Alcβ9-19 | 0.5 mg |
p3-Alcペプチドとは
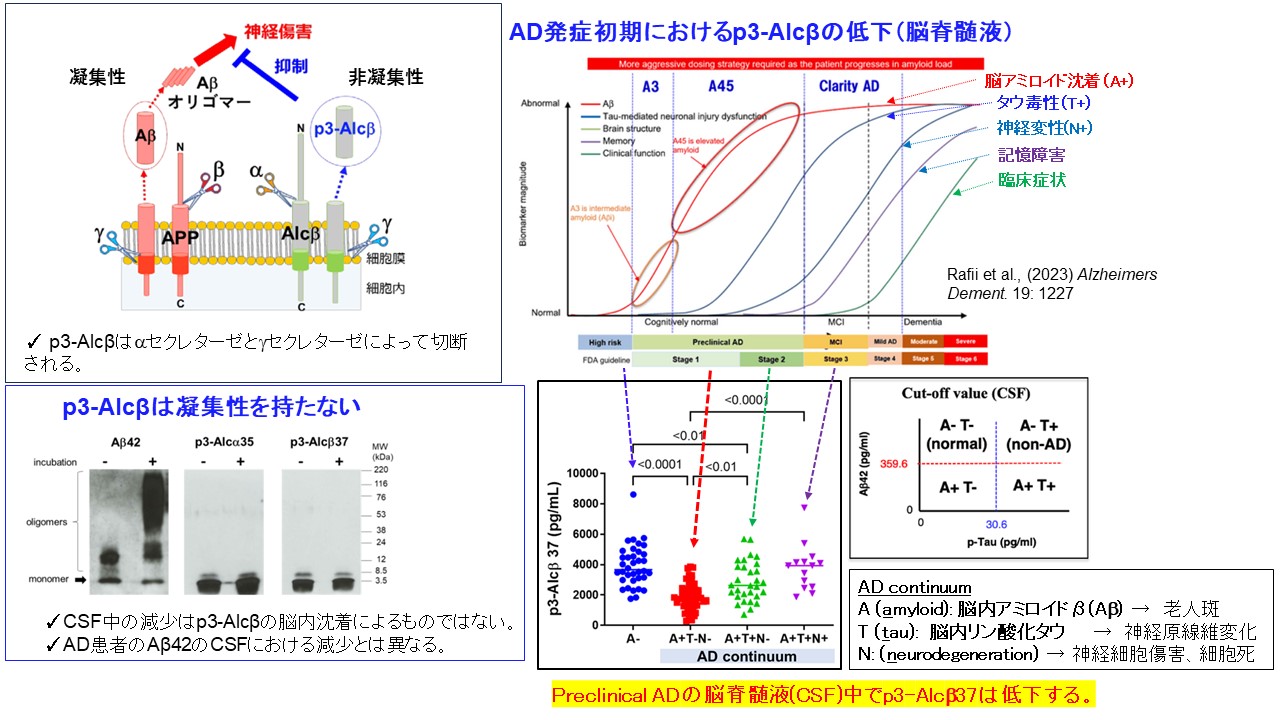
p3-Alcβ37は,神経細胞に高発現している,シナプス接着に関わるAlcadein β (Alcβ) / Calsyntenin 3 (Clstn3) という膜タンパク質が,Aβの前駆体タンパク質であるAPPを切断する酵素 β-secletase によって,同じ機構で切り出されることで生成されます2)。これまでの研究から,脳脊髄液中ではAβ1-40と同程度存在していますが,老化や,特にアルツハイマー病発症初期の患者の脳内ではp3-Alcβ37量が減少していることから,アルツハイマー病の病態との関連が示唆されていました3)。なお,このペプチド自体は,Aβと異なり凝集性がないことが確認されているため,アルツハイマー病患者の脳脊髄液中でのp3-Alcβ37量の減少は脳内沈着が原因ではないと考えられています。
p3-Alcβ37およびp3-Alcβ9-19の機能
Aβオリゴマーを処理したマウス初代培養神経細胞に対して,p3-Alcβ37およびその部分配列であるp3-Alcβ9-19を添加すると,細胞毒性が抑制されること,さらにはミトコンドリア機能の指標となるATPの産生量が増加することから,p3-AlcβペプチドがAβオリゴマーによる障害からミトコンドリアを保護し,神経細胞の生存率を高めていることが確認されました。
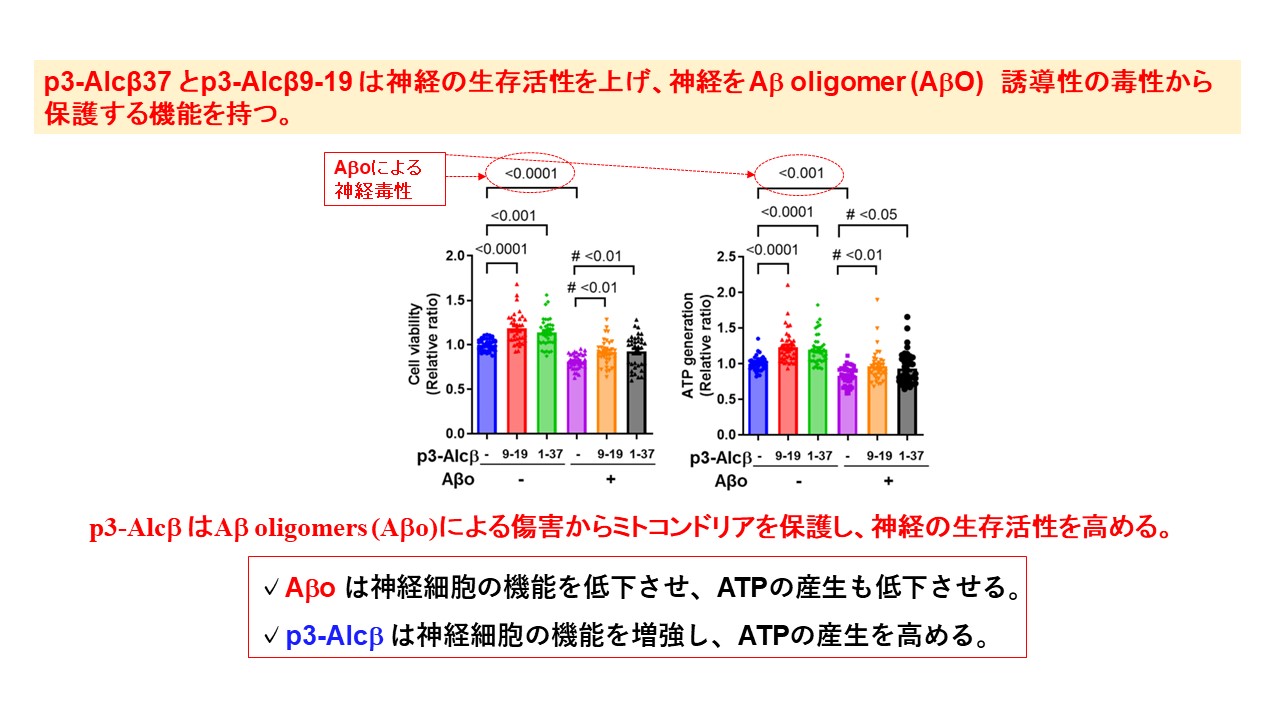
WT neurons (div15–20) were incubated for 24 h in the presence (10μM) or absence (-) of p3-Alcβ9-19 and p3-Alcβ1-37 with (+) or without (-) Aβ42 oligomers (Aβo, 2.5 μM). Neuronal viability was evaluated by MTT and ATP generation assays and expressed relative to neurons cultured in the absence of p3-Alcβ and Aβo (assigned a value of 1.0). Statistical significance was determined by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons tests (mean ± SEM; MTT: n=36, ATP: n=40). The significant P-values (<0.05, <0.01, <0.001, <0.0001) versus cells incubated in the absence (-) of p3-Alcβ and Aβo are indicated in the graphs. The significant P-values (#P<0.05, #P<0.01) versus cells incubated in the presence (+) of Aβo and in the absence (-) of p3-Alcβ are indicated in the graphs.
この神経細胞の保護作用は,p3-AlcβペプチドがAβオリゴマーによって誘発される細胞内へのCa2+の流入を抑制することに起因します。Aβオリゴマーは,神経細胞のNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体に作用して,細胞内に過剰なCa2+を流入させることが知られていますが,p3-Alcβペプチドを添加することで,細胞内へのCa2+の流入が有意に減少することが確認されています。

Suppression of Ca2+ influx induced by Aβo in neurons treated with p3-Alcβ9-19 and p3-Alcβ37. Mouse neurons (div 11–13) pretreated with Fluo 4-AM were stimulated at 5 min (arrow) with (+) or without (-) Aβo (5.2 μM) in the presence (+) or absence (-) of p3-Alcβ (50 μM). The fluorescence intensity was recorded at the indicated time (left) and the fluorescence area intensity for 18 min (5–23 min at time points) is shown (right) as the AUC expressed relative to that of cells cultured in the absence (-) of p3-Alcβ and Aβo (assigned a value of 1.0).
p3-Alcβ9-19の体内動態
p3-Alcβ9-19をマウスに皮下投与したところ,血中および脳脊髄液中にp3-Alcβ9-19が移行することが確認され,外部から投与したp3-Alcβ9-19が血中から脳中枢へと移行することが確認されています。
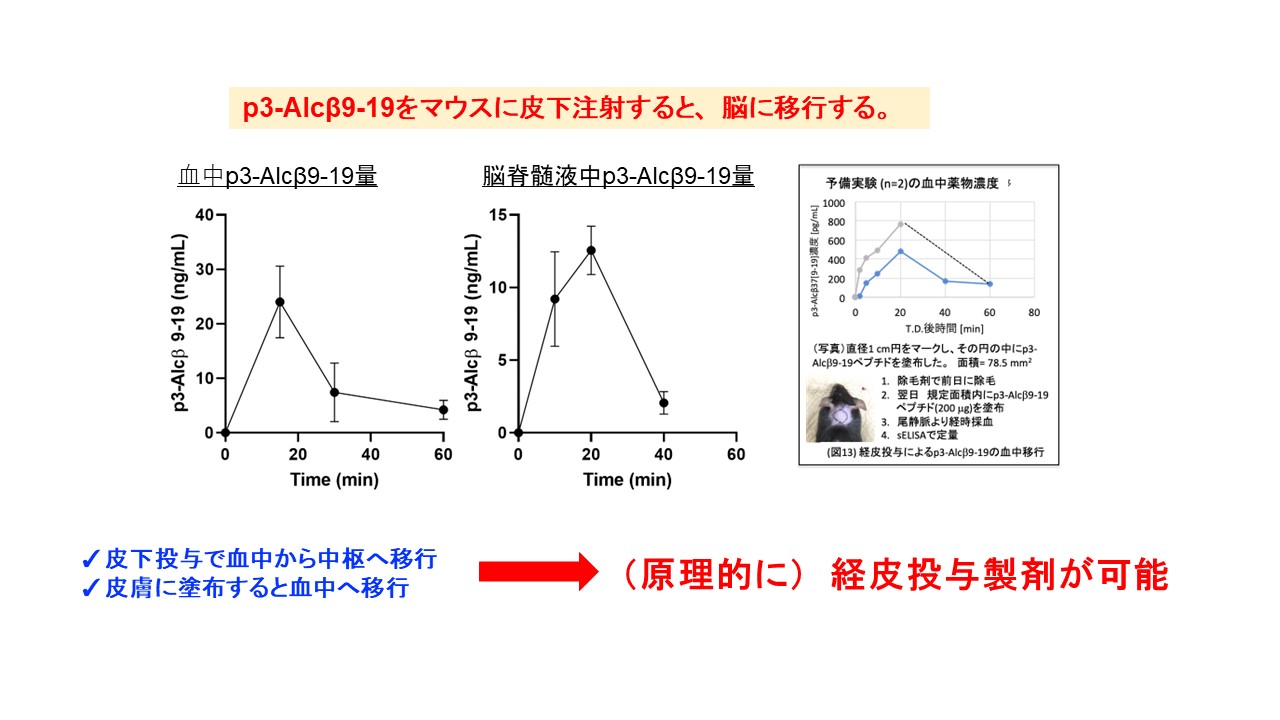
Sandwich ELISA for the quantification of p3-Alcβ9-19 and the determination of the pharmacokinetic profile of p3-Alcβ9-19. Transport of p3-Alcβ9-19 into the blood. p3-Alcβ9-19 (1 mg/kg of body weight, n = 4 per time point) was administered subcutaneously to wild-type (WT) mice (9-month-old). Blood was collected from their tail veins at the indicated time points, the plasma was diluted 200-fold, and p3-Alcβ9-19 concentrations were quantified by sELISA. Results are reported as mean±SEM. Transport of p3-Alcβ9-19 into CSF. p3-Alcβ9-19 (5 mg/kg body weight, n = 4 per time point) was administered subcutaneously to WT mice (5-month-old). CSF was collected from four mice, respectively, at the indicated time points and diluted 20-fold, and p3-Alcβ9-19 concentrations were quantified by sELISA. Results are reported as mean±SEM.
In vivoでのp3Alcβ9-19末梢投与の結果
p3-Alcβ9-19が脳中枢へと移行することが確認されたので,実際にアルツハイマー病モデルのマウスを用いて,脳内のミトコンドリア機能が回復しているかを調べました。[18F]BCPP-EFというプローブを用いたPETイメージングで,脳内のミトコンドリア機能を確認したところ,p3-Alcβ9-19を投与することで,ミトコンドリア機能が有意に回復することが確認されました。さらに,[11C]DPA713を用いたPETイメージングで,海馬での炎症が有意に抑制されることも確認されました。
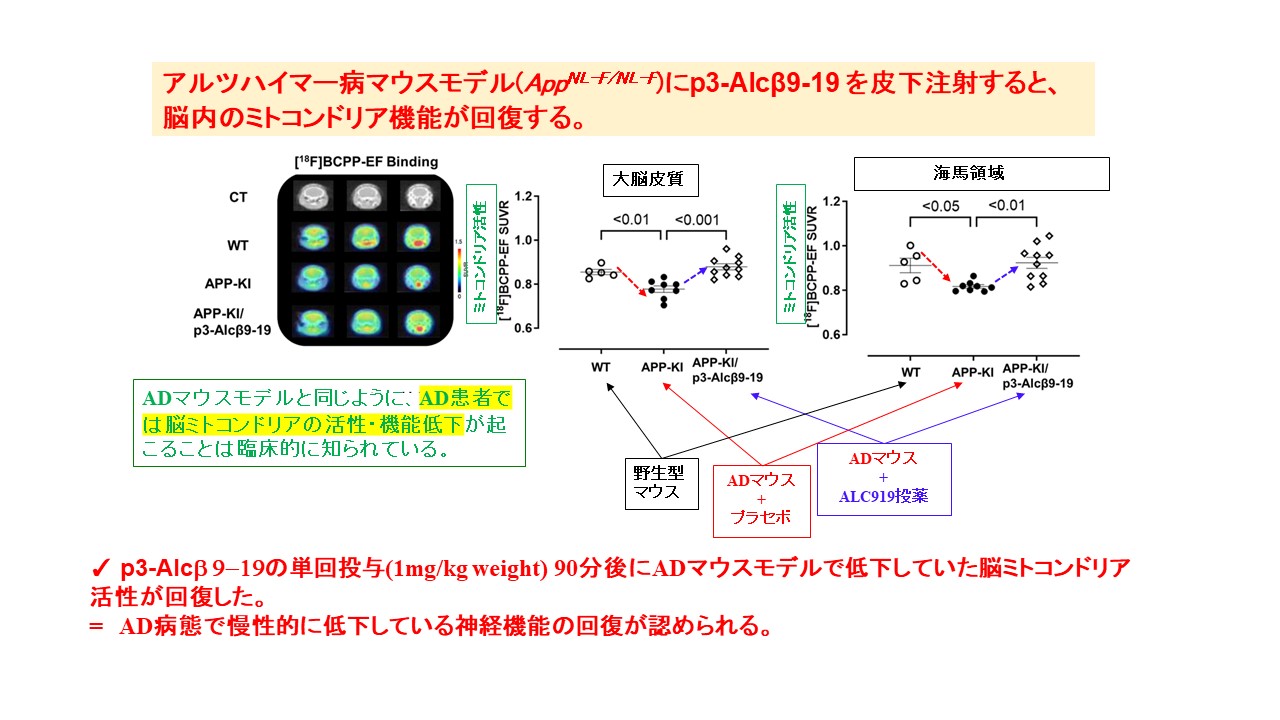
The SUVRs of [18F]BCPP-EF in the cortex and hippocampus of wild-type (WT) and AD mice (AppNL-F/NL-F) with (APP-KI/p3-Alcβ9-19) or without (APP-KI) a subcutaneous administration of p3-Alcβ9-19 (1mg/kg body weight). The PET data are superimposed on X-ray CT images, and the color bar denotes the SUVR.
The SUVRs of [18F]BCPP-EF in the cortex and hippocampus are compared across the three groups. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (mean±SEM; n=6–10), and significant P-values (P<0.05,P<0.01,P<0.001) are indicated on the graphs.
また,サルにp3-Alcβ9-19を単回,末梢投与した実験においても,脳内のミトコンドリア機能が活性化されることが確認されました。
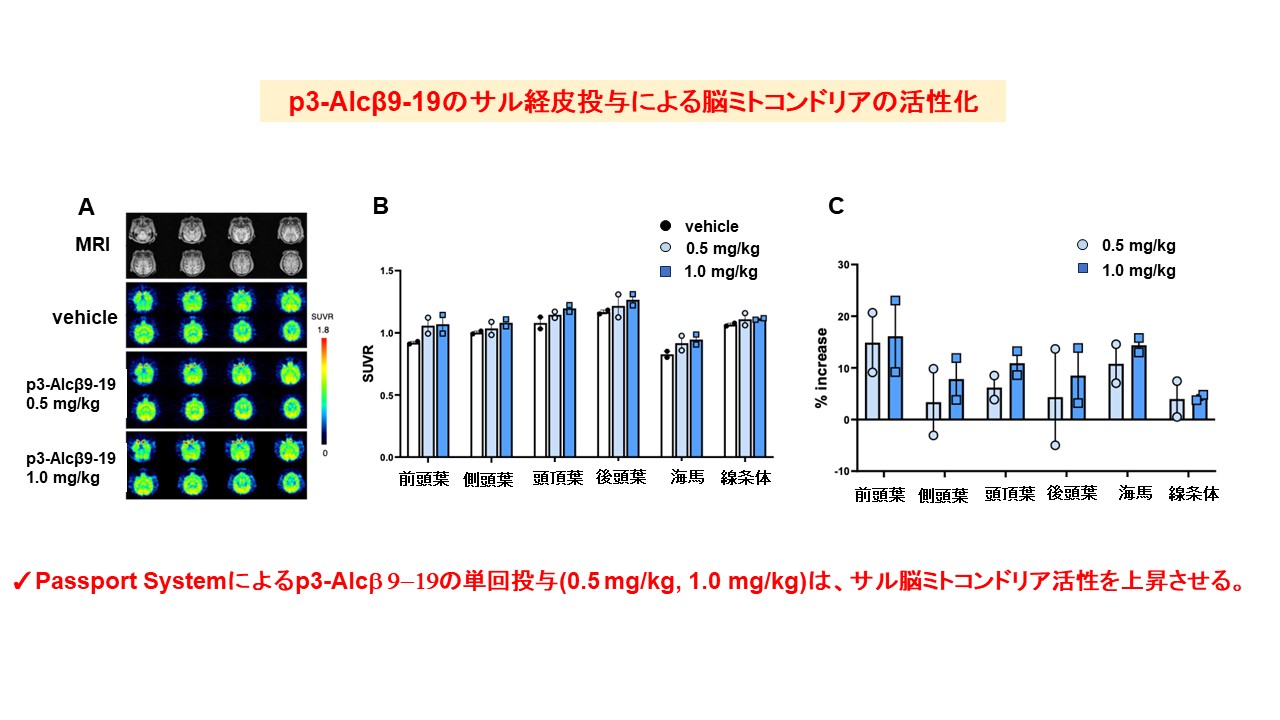
Increased mitochondrial activity after administration of p3-Alcβ9-19 to monkeys. Three consecutive PET scans in the same Rhesus monkeys (n=2) were performed after the transdermal administration of vehicle and p3-Alcβ9-19 (0.5 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg). The PET images of [18F]BCPP-EF SUVR were displayed in parallel with magnetic resonance (MR) images (A), and the color bar denotes the SUVR (B). The bar graph indicates the percentile increase in binding (C). Results are reported as mean±SEM (n=2).
データは北海道大学 鈴木利治先生 よりご提供いただきました。
・本製品は北海道大学より特許実施許諾を受けて,当社が製造販売を行っています。
・本製品は研究用です。研究目的以外には使用できません。
- Hata S et al., EMBO Mol. Med., 15, e17052 (2023).
- Hata S et al., J. Biol. Chem., 284(52), 36024-36033 (2009).
- Hata S et al., Alzheimers Dement (NY), 5:740-750 (2019).

